
Pr Oliver Nüsse, from University Paris-Sud, Orsay, France will present a strategic topic about ROS production in phagocytes during next ISANH Congress.
Phagocytes produce ROS to kill pathogens. How much radicals and which species are required for efficient killing is still under debate. How does the phagocyte “know” when to stop ROS production? What are the consequences of ROS escaping from the phagosome? To answer these questions, more accurate methods to detect ROS in time and space will be required. Future detection methods need to deal with the diversity of biologically relevant ROS, a wide range of concentration and with localized, short term production.
Among the last publications of Pr Nüsse:
ROS Production in Phagocytes: Why, When and Where?
Abstract
In the phagocytosis field, ROS production by the phagocyte NOX has been associated with pathogen killing for the last 50 years. Since the discovery of nonphagocyte NOX, numerous other roles for ROS production have been identified. Oxidative stress and ROS-mediated signaling have received much attention in recent years. Much lower concentrations of ROS may be required for signaling compared with microbial killing. Based on the discoveries in nonphagocytic cells, it became logical to look for ROS functions distinct from pathogen killing, even in phagocytes. ROS are now linked to various forms of cell death, to chemotaxis, and to numerous modifications of cellular processes, including the NOX itself. ROS functions are clearly concentration-dependent over a wide range of concentrations. How much is required for which function? Which species are required for how much time? Is ROS signaling only a side effect of bactericidal ROS production? One major obstacle to answer these questions is the difficulty of reliable quantitative ROS detection. Signal transduction often takes place on a subcellular scale over periods of seconds or minutes, so the detection methods need to provide appropriate time and space resolution. We present examples of local ROS production, decreased degradation, signaling events, and potentially ROS-sensitive functions. We attempt to illustrate the current limitations for quantitative spatiotemporal ROS detection and point out directions for ongoing development. Probes for localized ROS detection and for combined detection of ROS, together with protein localization or other cellular parameters, are constantly improved.
More information: www.isanh.fr
 It is a great pleasure to announce you the organization of 14th International Conference on Oxidative Stress Reduction, Redox Homeostasis and Antioxidants, which will be held in Paris, next June 12-13, 2014.
It is a great pleasure to announce you the organization of 14th International Conference on Oxidative Stress Reduction, Redox Homeostasis and Antioxidants, which will be held in Paris, next June 12-13, 2014. 
 The
The It is an honor to announce the award discerned by ISANH to Pr Katsuhiko Mikoshiba, M.D. Ph.D. Lab. for Developmental Neurobiology RIKEN Brain Science Institute, Saitama, Japan for all his scientific contributions in Neurodegenerative diseases researches.
It is an honor to announce the award discerned by ISANH to Pr Katsuhiko Mikoshiba, M.D. Ph.D. Lab. for Developmental Neurobiology RIKEN Brain Science Institute, Saitama, Japan for all his scientific contributions in Neurodegenerative diseases researches.
 Due to its 30 carbon double-bonds C60, the most abundant fullerene, is probably the most efficient free radical scavenger among all known chemical compounds. According to the literature, the range of possible actions of C60 and derivatives as free radical scavengers is impressive, notably in the fields of neurodegenerative disorders and ageing. However, although numerous experiments showed that C60 can efficiently scavenge a large variety of free radicals in vitro, the exact mechanism of its antioxidant action has never been demonstrated in vivo. Possible mechanisms of action remain to be investigated.
Due to its 30 carbon double-bonds C60, the most abundant fullerene, is probably the most efficient free radical scavenger among all known chemical compounds. According to the literature, the range of possible actions of C60 and derivatives as free radical scavengers is impressive, notably in the fields of neurodegenerative disorders and ageing. However, although numerous experiments showed that C60 can efficiently scavenge a large variety of free radicals in vitro, the exact mechanism of its antioxidant action has never been demonstrated in vivo. Possible mechanisms of action remain to be investigated.

 Dr Laurent Dupic, from Paris Hopitel Necker Hospital will give a translational talk focusing on oxidative mechanism and opening on therapeutic perspective.
Dr Laurent Dupic, from Paris Hopitel Necker Hospital will give a translational talk focusing on oxidative mechanism and opening on therapeutic perspective.
 Dr David Attaf, Paris, France, will highlight the impact of oxidative stress and inflammation on kidney diseases.
Dr David Attaf, Paris, France, will highlight the impact of oxidative stress and inflammation on kidney diseases. Dr Ramaroson Andriantsitohaina, from University of Angers, France will participate to the strategic discussion about
Dr Ramaroson Andriantsitohaina, from University of Angers, France will participate to the strategic discussion about 


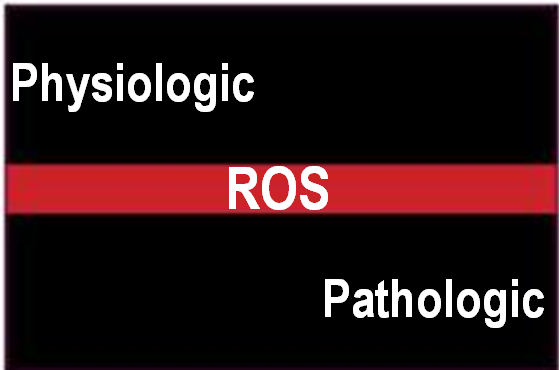 During Paris Antioxidants 2013, the Scientific Committee will discuss about the kind of strategies we need urgently to determine the basal level of ROS in healthy human which can be used to identify pathologic ROS in unhealthey subject and ultimately guide antioxidants treatment?
During Paris Antioxidants 2013, the Scientific Committee will discuss about the kind of strategies we need urgently to determine the basal level of ROS in healthy human which can be used to identify pathologic ROS in unhealthey subject and ultimately guide antioxidants treatment? During Paris Antioxidants 2013, our aim is to highlight the controversies of antioxidants activities and oxidative stress markers evaluation methods. In fact, the analysis of these markers can be realized by many different methods. But are these methods equivalent ? Which one is the best, the most representative? How to simply compare results coming from different methods?
During Paris Antioxidants 2013, our aim is to highlight the controversies of antioxidants activities and oxidative stress markers evaluation methods. In fact, the analysis of these markers can be realized by many different methods. But are these methods equivalent ? Which one is the best, the most representative? How to simply compare results coming from different methods? Paris Antioxidants 2013 will gather all actors of the world of oxidative stress and antioxidants:
Paris Antioxidants 2013 will gather all actors of the world of oxidative stress and antioxidants: 


 Please click here to purchase
Please click here to purchase


