Nicotinamide Riboside and Reactive Species Interactome: New Pathways in Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy
The Redox Medicine Society is pleased to announce an important international collaboration between leading research institutions: the University of Groningen Medical Center (UMCG), the National Institute on Aging in Baltimore, USA; the University of Copenhagen, Denmark; and the ISTCT, CNRS, Université de Caen Normandie, France. This study, led by Prof. Amalia Dolga’s lab at UMCG, explores the therapeutic potential of Nicotinamide Riboside (NR), a precursor of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), in preventing neuronal ferroptosis and modulating crucial biochemical pathways in the brain.
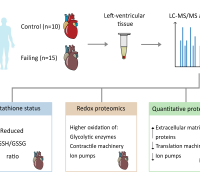
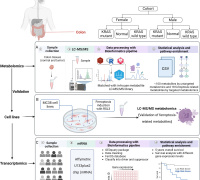
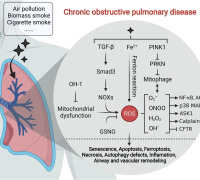
The research revealed that NR effectively prevents neuronal ferroptosis, a form of cell death linked to neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, NR modulates the bioenergetic status and reactive species interactome (RSI) within the brain, influencing critical aspects of cellular metabolism and stress response. The study also found that NR treatment leads to significant, region-specific changes in the brain’s proteomic landscape, particularly within the cortex and hippocampus, regions most affected by AD.
Moreover, the research established a correlation between protein co-expression modules altered by NR treatment and ATP production, along with various reactive species. These findings contribute to a deeper understanding of how NR influences the metabolome and proteome in Alzheimer’s Disease, potentially offering new avenues for disease modification and therapy.
Commenting on the study, Dr. Laurent Chatre, co-author and active member of the RMS Scientific Board, commented: “This paper opens up new perspectives on Alzheimer’s Disease, well beyond the traditional beta-amyloid-centered view, which has ultimately not led to therapeutic breakthroughs. The RSI and mitochondria are key players in this disease, presenting new opportunities for biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and personalized medicine”.
Read the full paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106645.
Photo credits: Dr. Laurent Chatre.