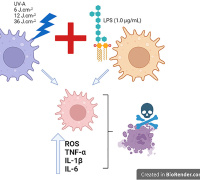
Effect of UV-A Exposure on Macrophages Previously Challenged with LPS in Terms of Oxidative Distress
News Release, Redox Medicine 2023 , France – March 10, 2023
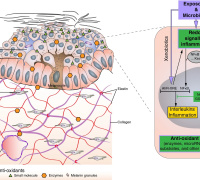
UV-A radiation affects skin homeostasis by promoting oxidative distress. Endogenous photosensitizers in the dermis and epidermis of human skin absorb UV-A radiation forming excited states (singlet and triplet) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) producing oxidized compounds that trigger biological responses.
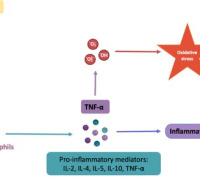
The activation of NF-kB induces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and can intensify the generation of ROS. However, there is no studies evaluating the cross talks between inflammatory stimulus and UV-A exposure on the levels of redox misbalance and inflammation.
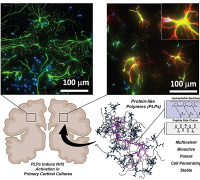
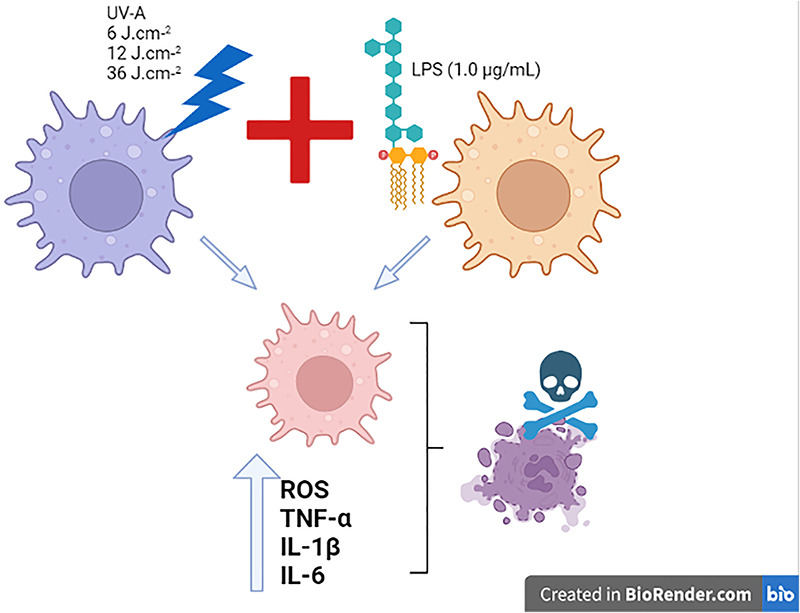
Maurício S. Baptista and his team evaluated the effects of UV-A exposure on J774 macrophage cells previously challenged with LPS in terms of oxidative distress, release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and activation of regulated cell death pathways.
Their results showed that LPS potentiates the dose-dependent UV-A-induced oxidative distress and cytokine release, in addition to amplifying the regulated (autophagy and apoptosis) and non-regulated (necrosis) mechanisms of cell death, indicating that a previous inflammatory stimulus potentiates UV-A-induced cell damage. They discussed these results in terms of the current-available skin care strategies.
Image credits: Chiarelli-Neto et al., Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology (2023)
Dr. Baptista will be a speaker at #RedoxMedicine2023 to discuss the skin redoxome. Submit a related abstract.
Media Contact:
Redox Medicine Society
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Redox Medicine 2023 Congress
June 21-23, 2023 - Paris, France
Website | LinkedIn | Facebook