Sulforaphane Protects Against Oxidative Stress & Mitochondrial Dysfunction Associated with Status Epilepticus
News Release, Redox Medicine 2023 , France – January 11, 2023
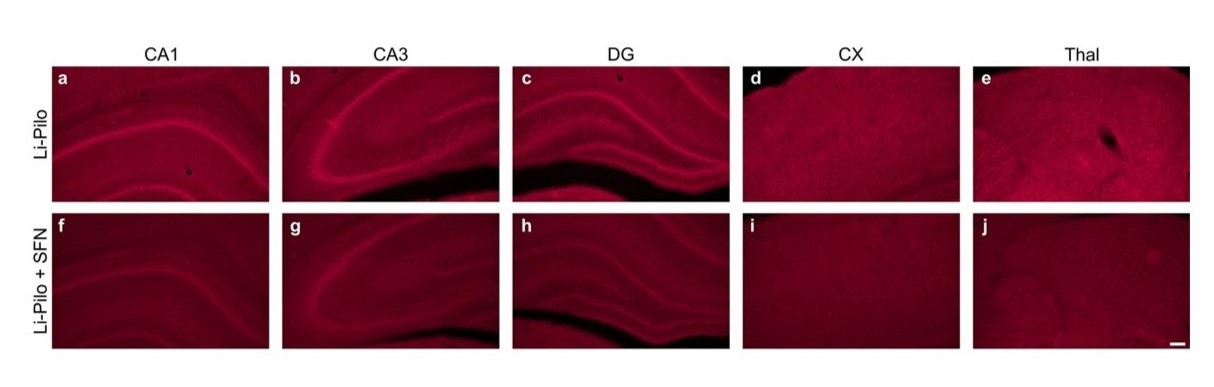 Fluorescence of the oxidized products of hydroethidium, assessed microscopically by fluorescence, in various brain structures following 60 min lasting SE induced by Li-pilocarpine (Li-Pilo)
Fluorescence of the oxidized products of hydroethidium, assessed microscopically by fluorescence, in various brain structures following 60 min lasting SE induced by Li-pilocarpine (Li-Pilo)
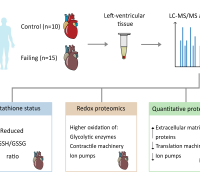
Dihydroethidium was employed for the detection of superoxide anions, immunoblot analyses for 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT) and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) levels and respiratory chain complex I activity for evaluation of mitochondrial function. Sulforaphane was given i.p. in two doses (5 mg/kg each), at PD 10 and PD 11, respectively.
Findings indicated that both the acute phase of SE and the early period of epileptogenesis (1 week and 3 weeks following SE induction) are associated with oxidative stress (documented by the enhanced superoxide anion production and the increased levels of 3-NT and 4-HNE) and the persisting deficiency of complex I activity.
Pretreatment with sulforaphane either completely prevented or significantly reduced markers of both oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Since sulforaphane had no direct anti-seizure effect, the findings suggest that the ability of sulforaphane to activate Nrf2 is most likely responsible for the observed protective effect.
Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway can be considered a promising target for novel therapies of epilepsy, particularly when new compounds, possessing inhibitory activity against protein–protein interaction between Nrf2 and its repressor protein Keap1, with less “off-target” effects and, importantly, with an optimal permeability and bioavailability properties, become available commercially.
Media Contact:
Redox Medicine Society
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Redox Medicine 2023 Congress
June 21-23, 2023 - Paris, France
Website | LinkedIn | Facebook